Rainfall

The drops which form clouds are in continuous movement, when these drops meet, they join together to form bigger, heavier drops, which the air can no longer hold, and so they fall in the form of rain.
Precipitation occurs as a result of ascending current of air, such ascent results in cooling and saturation of air. Further cooling leads to condensation. Ascent of air may take place under three different conditions in the atmosphere. These give rise to three major types of rainfall.

Types of Rainfall
Three broad categories are:
- Convectional Rainfall
- Geographic or Relief Rainfall
- Cyclonic Rainfall
Convectional Rainfall
In equatorial regions, there is uniformly high temperature throughout the year. This high temperature condition leads to intense heating of land and this heat is radiated towards the atmosphere. The hot air near the ground expands in volume and ascends to high levels and then ascending currents of hot and humid air result in condensation and formation of cumulo-nimbus clouds which give rise to torrential rainfall in the afternoon between 2 pm and 4 pm.
Geographic or Relief Rainfall
It occurs when the air is forced to ascend up the slope of mountain range or plateau which lies in its path. Such ascent leads to cooling of air causing condensation and precipitation. Precipitation is concentrated on Windward slope of mountain range which faces the wind. After precipitation it descends on the opposite or leeward side. Descend of air results in compression and air gets warmed up. Therefore, the Leeward side is relatively dry called rain-shadow region.
Cyclonic Rainfall
Cyclones are formed to fill up the intense low pressure developed due to differential heating of land and water. So, the air coming from the sea brings with them heavy rainfall. Tropical cyclones give rainfall to East Coast of continents in the tropical belt.
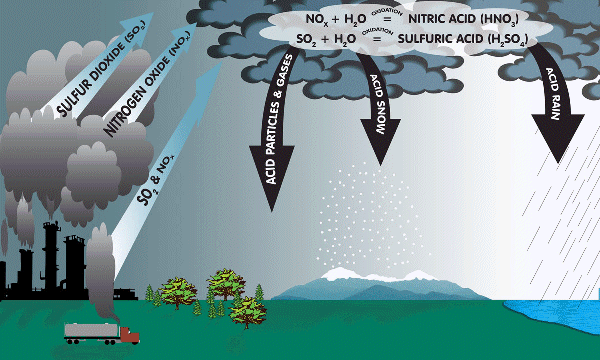
Acid Rain
Acid rain is the rain charged with an excessive amount of acid droplets formed when oxides of sulphur and nitrogen, released by burning of hydro carbons, are converted to acids in the atmosphere. It leaches minerals like calcium, magnesium from the soil, which are essential for plant growth.