Atmosphere

Life on Earth is not possible without the thick layer of Air which surrounds the Earth. This layer of Air is called the Atmosphere. The atmosphere is about 1000 km thick and is divided into five layers, each layer having different characteristics.
| Nitrogen: | 78.03 |
| Oxygen: | 20.99 |
| Argon: | 0.93 |
| Carbondioxide: | 0.03 |
| Hydrogen: | 0.01 |
| Others: | 0.01 |
The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night.
The presence of Oxygen in the atmosphere allows living things to breathe.
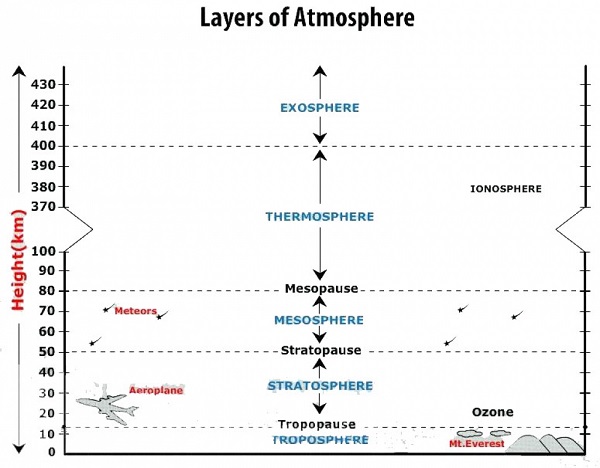
Structure Of Atmosphere
The Atmosphere can be divided into five layers:
 source:internet
source:internet
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere
- Exosphere
Troposphere
The layer nearest to the Earth’s surface is called the Troposphere. This is the most turbulent layer and is where our weather comes from. The gases which make up the atmosphere become thinner and thinner the higher up they are, before reaching Outer Space.
 source: internet
source: internet
The Troposphere is in contact with Earth’s surface. Here, the air is composed of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and thin gases and water vapor. This is where the wind, the rain and snow begin. In the higher zone of the troposphere the temperature reaches about -70degree C.
Tropopause separates troposphere from stratosphere. Height of troposphere change according to seasons, in summer it goes high, in winter down’s low.


